|
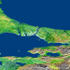
Mount Kilimanjaro (Kilima Njaro or "shining mountain" in Swahili), the highest point in Africa, reaches 5,895 meters (19,340 feet) above sea level, tall enough to maintain a permanent snow cap despite being just 330 kilometers (210 miles) south of the equator. It is the tallest free-standing mountain on the Earth's land surface world, rising about 4,600 meters (15,000 feet) above the surrounding plain. Kilimanjaro is a triple volcano (has three peaks) that last erupted perhaps more than 100,000 years ago but still exudes volcanic gases. It is accompanied by about 20 other nearby volcanoes, some of which are seen to the west (left) in this view, prominently including Mount Meru, which last erupted only about a century ago. The volcanic mountain slopes are commonly fertile and support thick forests, while the much drier grasslands of the plains are home to elephants, lions, and other savanna wildlife. This 3-D perspective view was generated using topographic data from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), a Landsat 7 satellite image, and a false sky. Topographic expression is vertically exaggerated two times. Photo Credit: NASA/JPL/NIMA [0003-0701-0121-3138] by 0003
|
Keywords
3d, africa, earth science, geography, jpl, kilima njaro, kilimanjaro, kilimanjaro tanzania, mount kilimanjaro, mount kilimanjaro tanzania, mount meru, mt kilimanjaro, mt kilimanjaro tanzania, mt meru, nasa, shining mountain, tanzania, triple volcano
|
|