|
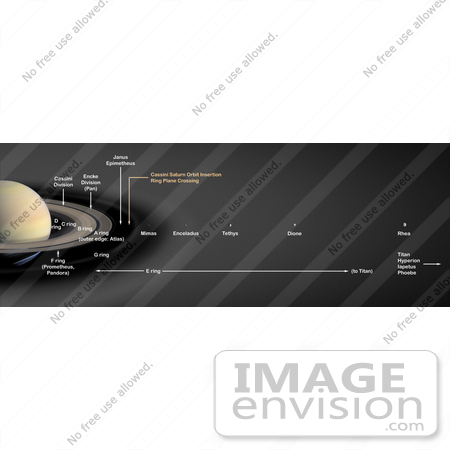
Royalty-free NASA stock photo of an artist’s concept of Saturn’s rings and major icy moons. Saturn’s rings make up an enormous, complex structure. From edge-to-edge, the ring system would not even fit in the distance between Earth and the Moon. The seven main rings are labeled in the order in which they were discovered. From the planet outward, they are D, C, B, A, F, G and E. The D ring is very faint and closest to Saturn. The main rings are A, B and C. The outermost ring, easily seen with Earth-based telescopes, is the A ring. The Cassini Division is the largest gap in the rings and separates the B ring from the A ring. Just outside the A ring is the narrow F ring, shepherded by tiny moons, Pandora and Prometheus. Beyond that are two much fainter rings named G and E. Saturn’s diffuse E ring is the largest planetary ring in our solar system, extending from Mimas’ orbit to Titan’s orbit, about 1 million kilometers (621,370 miles). The particles in Saturn’s rings are composed primarily of water ice and range in size from microns to tens of meters. The rings show a tremendous amount of structure on all scales; some of this structure is related to gravitational interactions with Saturn’s many moons, but much of it remains unexplained. One moonlet, Pan, actually orbits inside the A ring in a 330-kilometer-wide (200-mile) gap called the Encke Gap. The main rings (A, B and C) are less than 100 meters (300 feet) thick in most places, compared to their radial extent of 62,120 kilometers (38,600 miles). The main rings are much younger than the age of the solar system, perhaps only a few hundred million years old. They may have formed from the breakup of one of Saturn’s moons or from a comet or meteor that was torn apart by Saturn’s gravity. The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter was designed, developed and assembled at JPL. Photo Credit: NASA/JPL [0003-0712-1318-4938] by 0003
|